Jira Align Rest API reports HTTP 401 error
Summary
This article was explains the possible causes for receiving a 401 error when ujsing the Rest API with Jira Align.
Diagnosis
The typical error message is shown in the examples below:
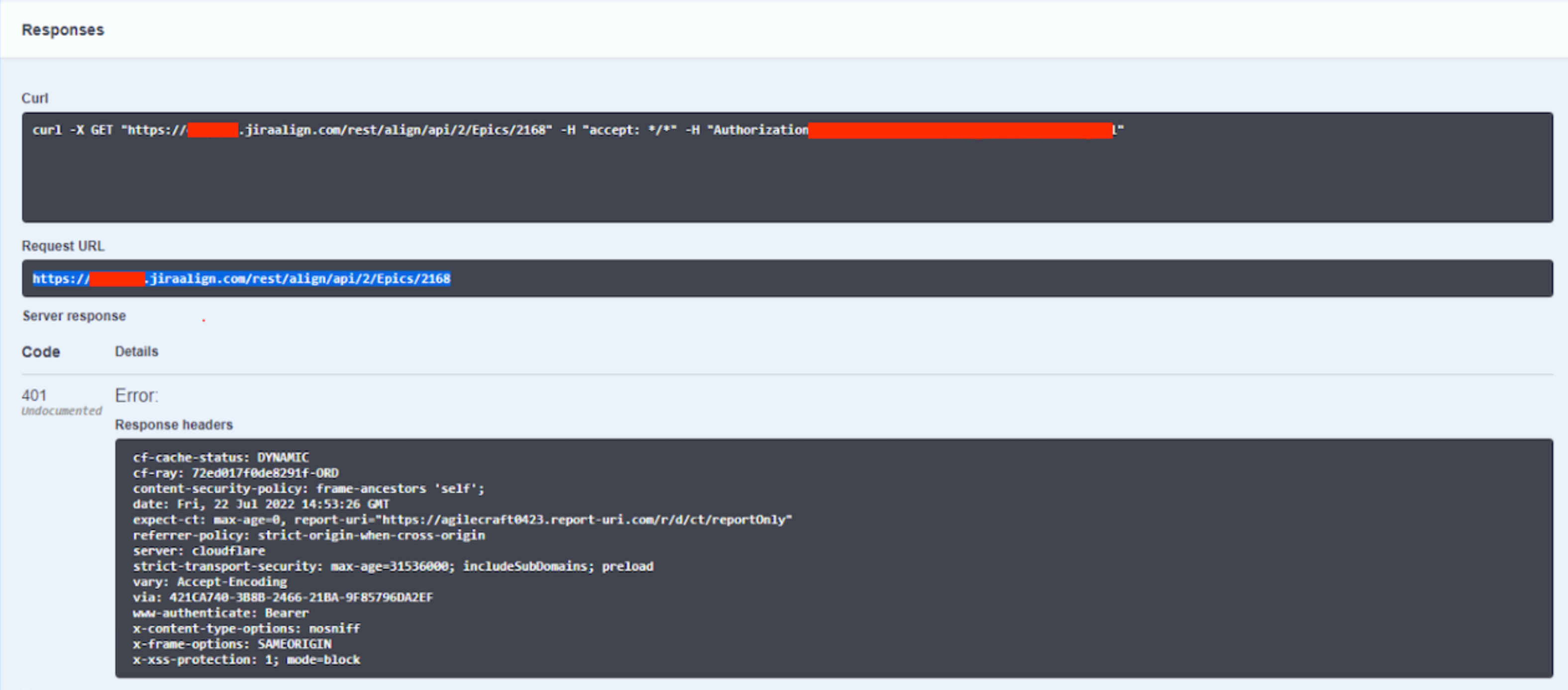
Error 401 from Swagger:
Cause
The 401 error is a common error in HTTP requests. This error indicates that the server received an unverified request.
In other words, it is as if the server the user is trying to access does not authorize the user's request. This "no authorization" can occur due to some factors, such as an incorrect URL, an invalid credential (API token typed in the wrong format, for example), DNS errors, firewall problems...
The 401 Unauthorized Error and the 403 Forbidden error are similar but different. While the 401 Error indicates that the server received an unverified request, a 403 error indicates that, although the client provided the needed authentication, they are still not allowed access to the requested resource.
Varying with the browser, the 401 error message may vary, like:
HTTP 401 Error – Unauthorized
401 Unauthorized
Access Denied
Error 401 Unauthorized
It is very common in Jira Align to encounter this error when users make calls to Jira Align Rest APIs.
Solution
The 401 error can be resolved with steps that depend on what is causing the "unverified" request. Therefore, when faced with an error like this, you will need to check a few things, as described below:
Credentials
⚠️ Note: Any examples of bearer tokens shown in this article came from a lab environment and have been reset, so they are no longer valid.
In Swagger ( https:// your JA server /rest/align/api/docs/index.html ), you must enter the correct credentials to authorize API calls:
Enter your credentials following the pattern bearer <API TOKEN>
To retrieve your API Token, go to Jira Align > User Menu > Edit My Profile
Click on API Token, and if you need it, click on Generate New API Token
Copy the string value contained in API 2.0 Token and precede it with the word “bearer ” in the Authorization Value, before clicking Authorize in the Swagger settings.
Example Value: bearer user:661800|LZy#Yfgmor[JS&okB7HTw~1oOHRc(5t!8hXXXxxx
Once you log in using credentials in the provided format, you will be able to use the API.
ℹ️ Note that the server response was 200, which means that the request was valid and, because of that, the server has processed and responded to the user’s request.
Firewall / Cloudflare
When an HTTP 403 error is received, this is likely to be caused by a firewall blocking, as the IP that the user is using is not allowed in the API's firewall rules.
However, sometimes a 401 Unauthorized error can be related to your firewall cache.
For example, the firewall may not be communicating correctly with the server, resulting in authentication errors. Assuming the credentials have been validated (as discussed above and the issue remains), then the fix for this firewall issue may require customers to contact our support teams, as it could be because:
There is a firewall API rule applied to the Jira Align Instance.
There is a cache problem with the firewall of the Jira Align instance.
There is a region block for the user’s IP Address.
Local Issues
It can also occur that only one computer/device is suffering from error 401, where users on other computers are able to use the API. The issue may then be related to some problem with the computer being used. Let's call this a "Local Issue”. Local issues only happen on one computer, which is affected among many others in a given environment.
Cache
Browsers store data so they don't have to load websites from scratch every time you access them. This is known as caching.
Invalid log-in information stored locally in your browser can disrupt the log-in process and, as a result, throw a 401 Unauthorized Error.
Fixing this issue is relatively simple. The majority of modern browsers let you clear your cache in a matter of a few minutes.
DNS
Another problem that can give us a 401 error is DNS errors. Although they are very rare, they can sometimes cause a 401 Error on your API call. To fix this, all you have to do is flush your DNS records.
Flushing your DNS records means deleting temporary data from a computer. The next time we try to access that problematic URL, it will make a completely new request and re-authenticate.
The process of flushing your DNS varies from one system to another:
If you're a Windows user, you need to open the command prompt and type in the CMD
ipconfig/flushdns.If you're a Mac user, you need to flush your DNS by typing in the command terminal
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder.For DNS issues, affected end users should contact their company's IT team to analyze and fix any probable DNS issues.
External References:
Was this helpful?